Introduction: Electronic Waste
Electronic products such as computers, cell phones, fax machines, stereos, VCRs, televisions, chips, copiers, and other related products that reach the end of their life become electronic waste products, which is known as E-waste. E-waste contains several hazardous substances such as heavy metals, lead, and mercury, as well as gold and other precious metals, which together form a massive amount of E-waste that can be extracted using advanced technology and used in the metal industry.
Table of Contents
- Introduction: Electronic Waste
- The Traditional Methods of Metals Extraction from E-waste
- Advantages of the E-extraction from E-waste
- Needs of the E-waste Management
- Kinds of e-Waste Products can be used in Metal Extraction Process
- Procedure for the Extraction of Metals from the E-waste
- Ways of Extraction
- Conclusion
--------------Blog Contact Form-------------
E-waste refers to all electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) that has been discarded by the owner, with or without the intention of reusing the product. Computers, mobile phones, televisions, stereos, fax machines, VCRs, and copiers are common terms for electronic products.
Electronic products contain some very harmful materials such as beryllium, mercury, cadmium, and lead. The materials might contain elements that add to the volume of the products and pose a threat to the environment. E-waste contains a large concentration of metals that can be extracted easily. A few of the processes for the extraction of precious metals are techniques, such as hydrometallurgy, pyrometallurgy, and biohydrometallurgy,
The Traditional Methods of Metals Extraction from E-waste
- Cyanide Usage
The use of cyanide in gold leaching has increased as a result of the mining industry, which is very beneficial. However, this method of metal extraction is extremely risky. E-waste and sodium cyanide are chemically combined in the process to create a soluble gold cyanide solution. This makes the extraction process very simple, despite the fact that the use of cyanide is restricted in some nations.
- Use of Acid
The use of acid, which combines hydrochloric acid and nitric acid, on e-waste has been found useful for the chemicals in the extraction of gold metals. Several other acids have been very useful in the extraction process of metals. The use of acids is comparatively less harmful than the use of cyanide for the dissolution of metals.
- Extraction Through the Bioleaching
The microbiological process for the extraction of metals such as gold, copper, palladium, silver, etc. is being used as an alternative to dangerous products such as cyanide and acid. In the process the Bacterias such as T. thiooxidans, Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, and fungi such as Penicillium simplicissimum, and Aspergillus niger, that extracts Zinc, Aluminium, Copper, Lead, etc.
Advantages of the E-extraction from E-waste
The recycling and reuse of e-waste through different mechanisms greatly reduce the amount of waste that is being deposited into the landfills of the world. Even for the sustainable development of the country and industry. The project will decrease the amount of waste that is dumped on the land. This ultimately results in the reduction of emissions of carbon dioxide and other harmful gases emitted from the mining of metals. Furthermore, the recycling of metals will increase the country's growth and economy.
Needs of the E-waste Management
More than 70% of e-waste is not recycled in its lifecycle and is dumped into landfills, and the incineration process generates a humungous amount of toxic gases in the atmosphere. E-waste contains metals and nonmetals which are valuable. The mining process is highly cumbersome and emits enormous amounts of dangerous gases. The management process, along with the recovery of the waste materials, helps in the protection of the environment.
Kinds of e-Waste Products can be used in Metal Extraction Process
- Circuit Boards
- Circuit Components such as Microchips, Ceramics, Carbon core, Aluminum heat sinks, capacitors, etc.
- Casings such as plastics casings on TV, household appliances, cell phone, and other steel or metallic cases
- Cathode ray monitor monitors
- Wire (used in wall sockets, power cords, internal wiring, charger, audio & video equipment
- Precious metals, such as gold are used in the Connection Pads & Solders for better electrical conductivity, the audio cables and cell phone batteries are common examples of the same, Battery contains silver products, and Palladium is used in switches, Capacitors, and Solder pads, etc.
Procedure for the Extraction of Metals from the E-waste
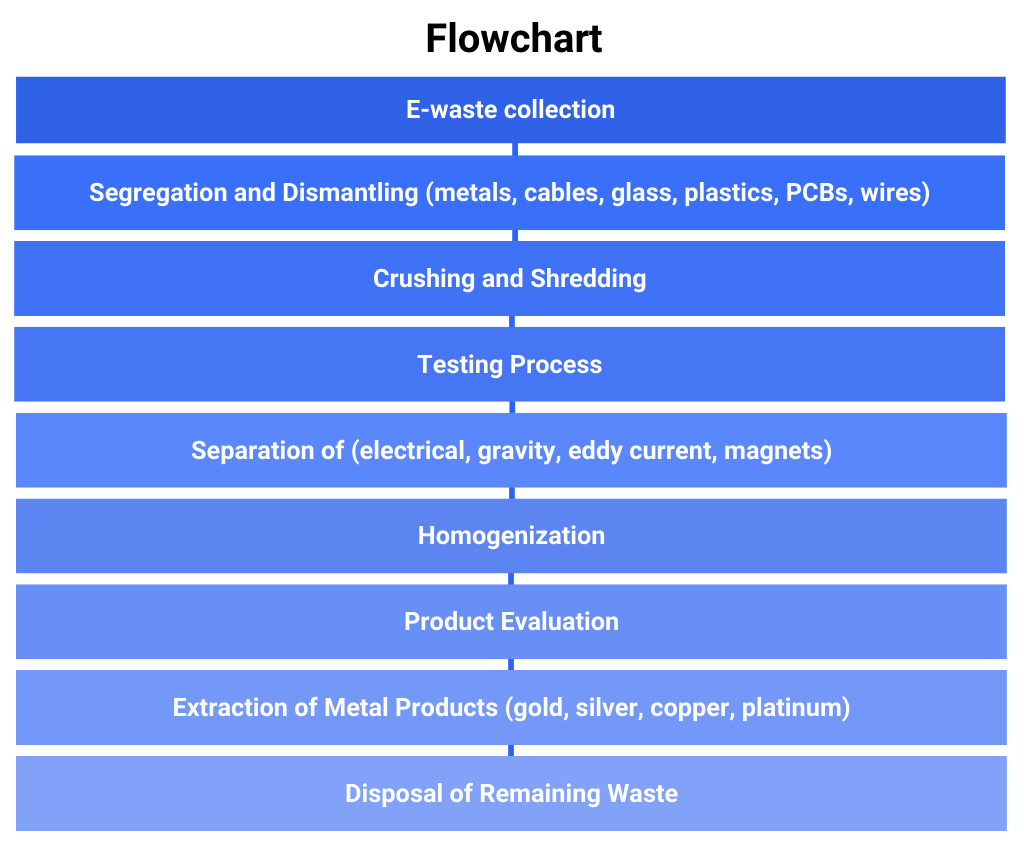
Ways of Extraction
- Hydrometallurgy
- Pyrometallurgy
- Biohydrometallurgy
Hydrometallurgy
In the hydrometallurgy process, metals are extracted from ores using an aqueous solution. Hydrometallurgy includes the leaching process for the dissolution of metals and aqueous solutions. The solution gets separated from the ores and solid materials, which go through the process of purification and concentration so that metal can be extracted, in the form of chemical products or metallic states.
Distillation, precipitation, adsorption, and solvent extraction are all part of the concentration process. The extraction of metals through leaching, purification, and recovery comes after the first stage of base metal recovery.
Pyrometallurgy
It is the process of recovering non-ferrous and priceless metals from products made of e-waste. The treatment process works at high temperatures, melting, incineration, etc. Due to the availability of PCB, this process is no longer a good method of extraction. as it produces very toxic and carcinogenic compounds. This is the process that is more exact, predictable, and controlled.
The Biological Leaching Process or Biohydrometallurgy
The microbiological leaching process is the natural ability of microorganisms to transform metal into waste and solid form and dissolve the matrix. The bioleaching process of alkaline and the leaching process biologically in an acidic environment is the role of the biohydrometallurgical process. The bacteria used in the process are Acidophilus and Chemolitthotrophic Microbial consortia, Acidiobacillus thiooxidans, Acidiobacillus ferrooxidans, and heterogeneous substances such as Sulfolobus, Penicillium (fungi), and Aspergillus Nigerare (eucaryotic microorganisms), which are used in the bioleaching process from the waste products.
Conclusion
One of the biggest challenges in the world is the growing e-waste and the loss of several precious metals through e-waste. Hazardous products and materials cause a threat to the lives of human beings and other living habitats. The waste products must be treated for reuse and recycling instead of putting them off to dump sites or landfills. Even if there are still waste products that can't be recycled, they should go through the extraction process for any precious metals and other elements that might be present. This mechanism both conserves natural resources and creates new business opportunities for the modern era. By using these strategies, environmental and health problems can be reduced while also allowing for only environmentally friendly growth.
E-Waste
E-waste recycling in India is important to reduce electronic waste, recover valuable resources, and promote sustainable growth. The e-waste recycling plant helps to minimise e-waste and collect valuable metals to be used later.
Battery Waste Management
Batteries (Management & Handling ) Rules apply to every manufacturer, importer, re-conditioner, assembler, dealer, recycler, auctioneer, consumer and bulk consumer involved in manufacture. Team Corpseed will help you to draft and submit online & offline application to respective SPCB and CPCB.
E-Waste Dismantling
The E-Waste rules apply to every manufacturer, producer, consumer, bulk consumer, collection centers, dealers, e-retailer, refurbisher, dismantler and recycler involved in manufacture, sale, transfer, purchase, collection, storage.
This portion of the site is for informational purposes only. The content is not legal advice. The statements and opinions are the expression of author, not corpseed, and have not been evaluated by corpseed for accuracy, completeness, or changes in the law.
BOOK A FREE CONSULTATION
Get help from an experienced legal adviser. Schedule your consultation at a time that works for you and it's absolutely FREE.









.webp)