
Loading...
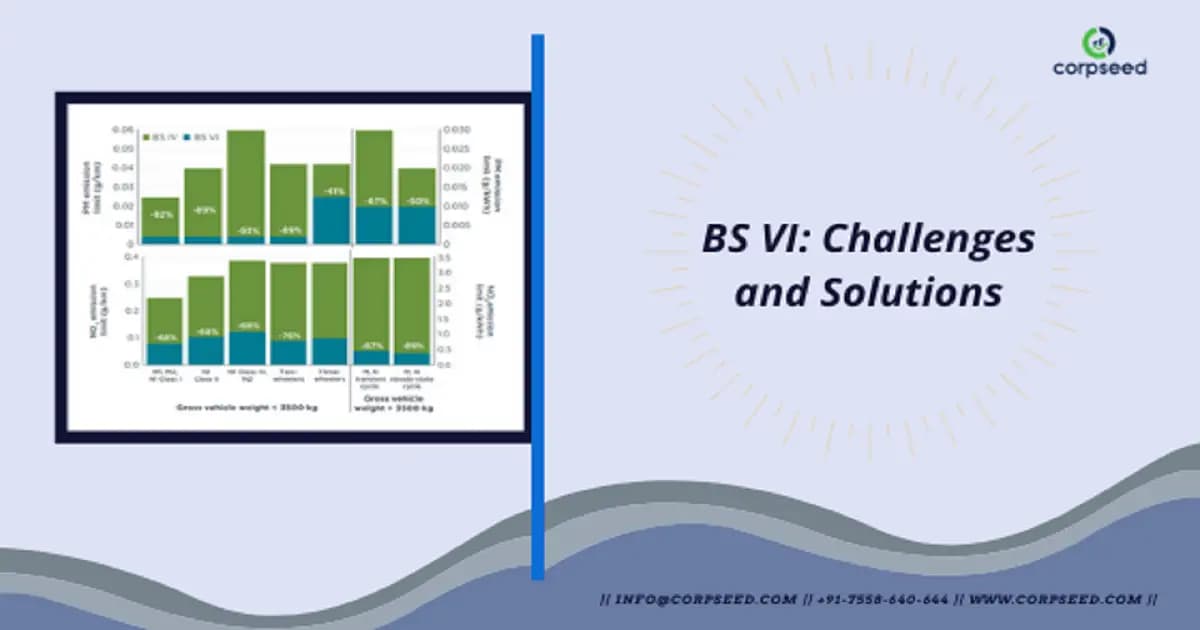
The enormous distinction between BS IV and BS VI grade fuel will be sulfur content,The sulfur content in BS VI grade fuel will be only one-fifth of that in BS IV fuel.
About the Author

Experienced Digital Marketer with a demonstrated history of working in the Internet industry. He likes to write about the latest technology trends, Skilled in Digital Marketing likes. Search Engine Optimization, SMO, SEM, PPC, Content Writing, and, Designing, etc.
Related articles

How To Register A Startup Under Startup India?
2026-12-31

How to Register on the GeM Portal?
2025-12-26

How to Find the Right NIC Code for Udyam Registration (Step-by-Step Guide)
2025-12-16

How SARAL SIMS Changes Import Clearances for MSMEs
2025-12-03

DPIIT Registration: Benefits, Eligibility, Fee, and Complete Process
2025-11-24

MSTC License for Scrap: Complete Guide for Registration, Benefits & Process
2025-11-20
CDSCO Releases New Guidelines for Compounding of Offences Under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act
2026-02-26 • 0 views
2023-02-27
2026-02-26