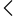The carbon footprint shows the total greenhouse gas emissions generated by mining activities, including carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and fluorinated nitrous oxide (N2O). These emissions are categorized into three scopes on the basis of their origin and control.
Calculating the carbon footprint permits organizations and individuals to identify major emission sources, which are hotspots, and implement strategic intrusions to reduce emissions. This comprehensive approach not only helps achieve sustainability goals but also contributes to global efforts to mitigate climate change by outlining the environmental costs of regulatory activities and decisions. Programs like LEED Zero carbon certification reassures businesses to actively track and neutralize their footprint by applying carbon reduction and recovery practices.
What is a Carbon Footprint and why is it Important?
The carbon footprint represents the total emissions of greenhouse gases, which include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O) and fluorinated gases, related to human activities. These emissions are classified into three scopes:
- Scope 1: Direct emissions from owned or controlled sources (e.g., vehicles, factories).
- Scope 2: Indirect emissions from purchased electricity, steam, heating, and cooling.
- Scope 3: All other indirect emissions in the value chain, such as transportation, business travel, and waste disposal.
By calculating the carbon footprint, organizations and individuals can classify emission hotspots and develop targeted strategies to reduce environmental impact.































































-Limited.webp)












-Private-Limited.webp)






-Private-Limited.webp)





















Pvt.Ltd.webp)








-Private-Limited.webp)